The Role of Genetics in Pancreatic Cancer Risk
Understanding the factors that contribute to pancreatic cancer risk can guide individuals in making informed decisions about their health and well-being. Among the many influences on the development of cancer, genetics plays an integral role. It can be helpful to understand what causes cancer in the pancreas and how genetics can impact predisposition to it.
Pancreatic Cancer
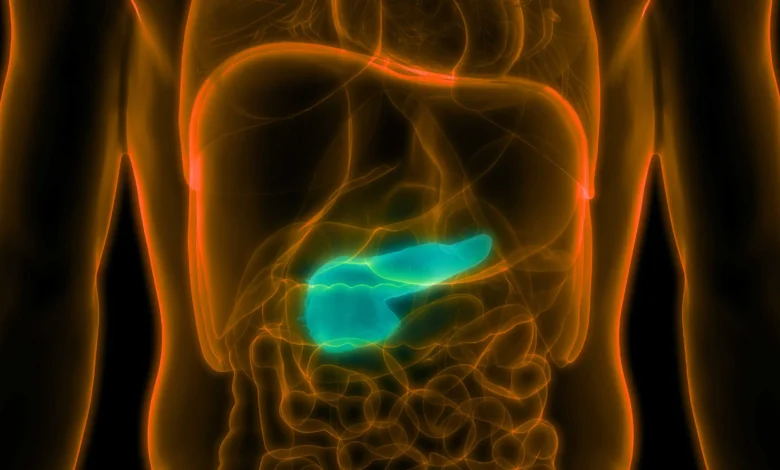
Pancreatic cancer occurs in the tissues of the pancreas, which is a vital organ responsible for aiding digestion and regulating blood sugar. It is not as common as some other forms of cancer. Its complex nature and often late-stage diagnosis can make it a challenging disease to manage.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Individuals with pancreatic cancer may experience symptoms that include abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, jaundice (yellowing of the skin), and digestive problems such as nausea. These symptoms are non-specific, meaning they may also occur in less serious conditions, making early detection more difficult. Diagnosis begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Imaging studies such as MRI or ultrasounds are often used to identify abnormalities in the pancreas. Given the non-specific nature of its symptoms, individuals are encouraged to seek medical advice if they notice persistent changes in their health.
Impact of Genetics
While many risk factors for cancer are widely acknowledged, genetics is a factor that warrants closer examination. Research indicates that inherited genetic mutations can increase the likelihood of developing this cancer. These mutations may either occur spontaneously or be passed down through family lines.
Genetic Mutations and Syndromes
Certain genetic mutations, such as BRCA mutations, are linked to certain forms of cancer. Individuals with these mutations have a higher likelihood of developing cancer in their pancreas within their lifetime. Inherited conditions such as hereditary pancreatitis are also associated with an increased risk. These syndromes are caused by specific genetic mutations that are identifiable through genetic testing.
Family History
A strong family history of pancreatic cancer is also a known indicator of genetic influence. Individuals with two or more first-degree relatives diagnosed with a pancreas afflicted by cancer may be part of a familial cancer cluster. Research continues to better understand the genetic markers that contribute to these familial links.
Research and Future Perspectives
Advancements in genetic research continue to shed light on how specific gene variations interact with other factors to influence cancer risk. This is paving the way for more targeted approaches to prevention, early detection, and treatment. Genetic tests that screen for mutations associated with pancreatic cancer can help individuals who may require closer medical monitoring.
Know When to Seek Medical Care
Genetics is a foundational aspect of understanding cancer risk, but it is not the sole factor. Those concerned about their genetic predisposition or experiencing symptoms associated with pancreatic cancer are encouraged to consult healthcare providers. Regular check-ups, coupled with open discussions about family medical history, can help tailor a preventive health plan. For those who may benefit from genetic counseling or testing, healthcare professionals can guide the next steps. Awareness and proactive action can play a significant role in navigating health concerns, potentially leading to earlier detection and better management of cancer.