Nuclear Stress Tests: A Non-Invasive Tool for Evaluating Heart Function

Evaluating heart health is a key aspect of maintaining overall well-being. When specific tests are needed to assess the heart’s condition during physical exertion, a nuclear stress test often serves as a non-invasive and effective option. This test provides insights into how the heart performs under stress, offering medical professionals a deeper understanding of cardiac function. Here is more information on what this type of test entails, why it is conducted, what occurs during the procedure, and the potential benefits of undergoing this type of assessment:
What Is a Nuclear Stress Test?
A nuclear stress test is a diagnostic imaging test used to evaluate blood flow to the heart. The test is performed both during rest and while the heart is under physical or pharmacological stress. It involves the use of a small amount of radioactive material, called a tracer, which highlights blood flow in specific areas of the heart.
Images are captured with a special camera to identify areas where blood flow may be reduced. These results allow healthcare providers to assess if the heart is receiving adequate oxygen and nutrients. This is especially useful to evaluate during periods of increased activity.
Why Is This Test Conducted?
These tests are typically conducted to evaluate specific concerns regarding heart health. They can indicate whether blockages are reducing blood flow to the heart muscle or if there are regions of the heart that have been damaged by a previous event, such as a heart attack. Doctors may recommend this test as a way to assess the severity of symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or fatigue. It can also help evaluate the effectiveness of treatments, such as medication or stent placement, and determine whether further procedures may be necessary.
What Happens During This Test?
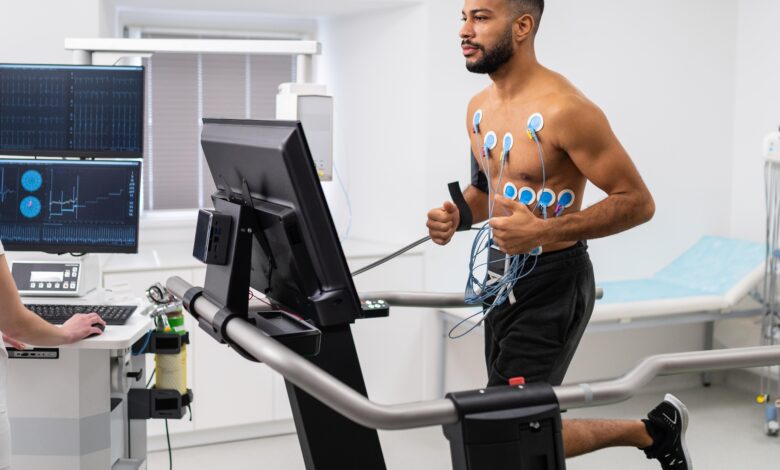
A nuclear stress test generally has two phases: resting and stress testing. Each phase involves the injection of a radioactive tracer into the bloodstream. During the resting phase, images of the heart are captured while the body is relaxed. This provides a baseline of the heart’s blood flow.
For the stress phase, the patient may walk on a treadmill or receive medication that mimics the heart’s activity during exercise. Additional tracer is administered, and images are taken while the heart is under physical or simulated stress. The captured images from both phases allow practitioners to compare blood flow to the heart under different conditions, helping identify potential areas of concern. The entire procedure is conducted under medical supervision and typically lasts a few hours, with minimal physical discomfort.
Why Is Getting Tested Beneficial?
These tests provide a detailed and comprehensive view of how the heart performs during physical activity. This level of detail helps identify issues that may not be detected through routine examinations or standard ECG tests. These tests can assist in planning for future care and guiding decisions on lifestyle improvements, medical treatments, or surgical interventions. They also allow monitoring of ongoing conditions, making sure that treatment plans are working effectively.
Seek Medical Guidance Today
Nuclear stress tests are a valuable tool for evaluating cardiac function in various situations. They offer detailed information about blood flow to the heart. This supports informed and timely medical decisions.
While this test is conducted under medical supervision and integrates advanced imaging technology, it’s always best to discuss with a healthcare provider whether this diagnostic method aligns with individual health needs. If you’re thinking about scheduling this test or looking for more information, contact your healthcare provider. Explore how this evaluation might support your heart health.