Minimally Invasive Treatments for Persistent Lower Back Pain
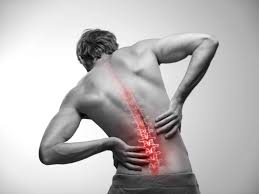
Persistent lower back pain is a problem that can affect daily life. While occasional discomfort is normal, chronic pain may indicate underlying conditions requiring a focused approach. Minimally invasive treatments are a favorable option for managing pain in the lower back without traditional surgery. Here is more information on back pain, causes, symptoms, and minimally invasive procedures that may provide relief:
What Is Lower Back Pain?
Lower back pain refers to discomfort or stiffness experienced in the lumbar region, the part of the spine located between the ribcage and pelvis. It can range in severity, from mild aches to intense, persistent pain that affects mobility and overall quality of life. Pain in the lower back may be characterized as acute when lasting a few days to weeks or chronic when it persists for longer periods, often exceeding three months. Chronic pain may require professional evaluation and management to alleviate symptoms effectively.
What Are the Causes and Symptoms?
Lower back pain may result from a variety of causes, including injury, strain, or underlying medical conditions. Common factors include herniated discs, muscle or ligament strains, arthritis, or conditions like spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal). Poor posture, obesity, or repetitive movements may also contribute to chronic lower back discomfort.
Symptoms associated with lower back pain may include dull aches, sharp localized pain, radiating pain into the legs (sciatica), or stiffness that limits movement. Individuals might also experience numbness or tingling, particularly if nerve compression is involved. Consulting a healthcare provider can help pinpoint the cause and determine appropriate treatments.
What Are the Minimally Invasive Treatments?
Minimally invasive treatments focus on alleviating pain while reducing recovery times and risks associated with traditional surgery.
- Epidural Steroid Injections: These injections deliver anti-inflammatory medication directly to the affected spinal area. They help reduce swelling and manage pain caused by nerve irritation.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): This technique uses heat generated by radio waves to target and disable pain-transmitting nerves. It offers longer-lasting relief for certain conditions.
- Nerve Blocks: These injections are designed to interrupt pain signals carried by specific nerves. They are often used to diagnose the source of pain and provide temporary relief.
- Spinal Cord Stimulation: This procedure involves implanting a device that sends electrical impulses to the spinal cord to reduce pain signals. It may be recommended for chronic pain conditions that haven’t responded to other treatments.
These treatments should always be conducted under the guidance of a qualified specialist. Further evaluation may identify which approach matches an individual’s condition.
When Should You See a Specialist?
While occasional back pain can sometimes be managed with over-the-counter medication or physical therapy, persistent or severe pain may require professional attention. Signs such as worsening pain, numbness, weakness, or loss of bladder or bowel control warrant urgent evaluation by a specialist. It is beneficial to consult a healthcare provider if back pain interferes with daily activities or does not improve over time. Early intervention can help prevent the progression of underlying conditions and explore minimally invasive options tailored to specific needs.
Seek Guidance Today
Persistent pain in the lower back can be challenging, but minimally invasive treatments offer an opportunity for relief without significant disruption to daily life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available options, individuals can make informed decisions about their care. Consulting a specialist is the first step toward a personalized treatment plan. Seek professional advice today to explore treatment options that could improve your mobility and functionality.