How Tendonitis Affects Different Parts of the Body
Tendonitis is a condition that results from the inflammation of a tendon, which connects muscle to bone. It often develops due to repetitive motions or overuse. This condition can impact various body parts, presenting different challenges depending on its location. Whether you’re an athlete, an active individual, or a healthcare professional, understanding how tendonitis can manifest in other areas can help with prevention and management.
In the Shoulder
Shoulder tendonitis, commonly referred to as rotator cuff tendonitis, affects the tendons around the shoulder joint. The rotator cuff helps stabilize and move the shoulder, which means tendonitis in this area can limit mobility and cause pain. Activities that involve repetitive overhead motions, such as swimming or painting, can increase the likelihood of developing this condition. Many individuals report discomfort when raising their arms or lifting objects.
In the Elbow
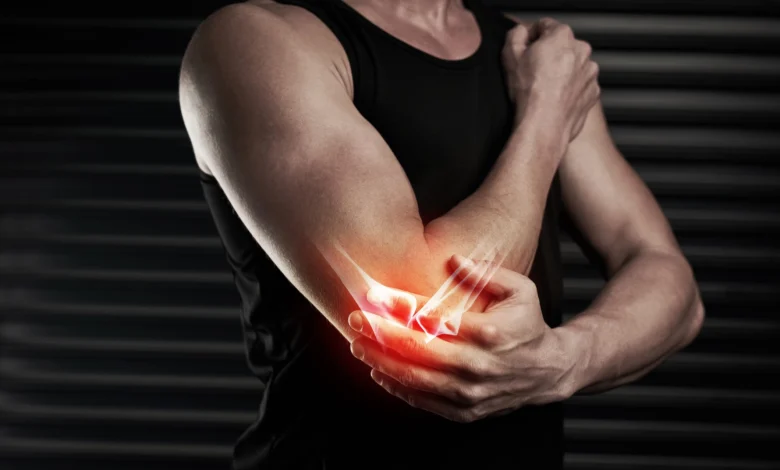
Commonly known as “tennis elbow” or “golfer’s elbow,” elbow tendonitis develops due to overuse of the tendons connected to the elbow. Despite the names, this condition isn’t exclusive to athletes. People who perform repetitive tasks, like typing or gardening, are also at risk. This occurance in the elbow may result in pain radiating from the elbow down the arm. It generally worsens with activities that involve gripping or lifting.
In the Wrist
Wrist tendonitis is often triggered by repetitive hand motions or prolonged use of a keyboard or mouse. This condition can lead to stiffness and pain in the wrist, making daily tasks such as writing or lifting difficult. Individuals experiencing wrist tendonitis might notice swelling around the wrist or a weak grip.
In the Knee
Knee tendonitis, or patellar tendonitis, affects the tendon that connects the kneecap to the shinbone. Those who engage in activities like running, jumping, or cycling are more likely to experience this condition. Symptoms often include pain at the front of the knee and tenderness around the kneecap. The discomfort usually increases after physical activity or climbing stairs.
In the Achilles
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body, connecting the calf muscles to the heel bone. Achilles tendonitis typically occurs in runners or individuals who frequently walk or stand for extended periods. Pain is often felt at the back of the ankle and may worsen during physical activities. Tight calf muscles or improper footwear can also contribute to the development of this condition.
In the Hip
While less common, tendonitis in the hip can impact those who perform repetitive hip flexion movements. This condition leads to discomfort in the groin area or front of the hip. Symptoms may include a snapping sensation when moving the hip or difficulty participating in activities that involve running or climbing.
Managing Tendonitis
Preventing tendonitis begins with avoiding repetitive activities or modifying movements to reduce strain on tendons. Proper stretching and strengthening exercises can also help protect tendons in vulnerable areas. Resting the affected area and seeking medical advice can help manage symptoms and support recovery if you suspect tendonitis.
Understanding how this impacts different parts of the body can be a step in addressing its effects. With appropriate care and adjustments, many individuals can continue to maintain their active lifestyles.