How Dermatology Innovations Are Revolutionizing Skin Cancer Treatment
Advances in dermatology have significantly enhanced the way skin cancer is detected, diagnosed, and treated. Through technological innovations and evolving research, clinicians and researchers are discovering novel methods to improve patient outcomes while minimizing invasive procedures. Here is some information that explores how modern dermatology is transforming skin cancer care and what these breakthroughs mean for healthcare.
Diagnostic Tools for Early Detection
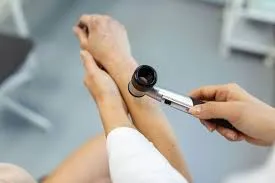
Early detection is pivotal in improving outcomes for individuals with skin cancer. Dermatology specialists are leveraging artificial intelligence to increase diagnostic accuracy. AI systems analyze medical imaging, such as dermoscopy images, to identify potential signs of skin cancer. These tools have been trained on thousands of case studies, allowing them to recognize patterns and abnormalities difficult to detect with the naked eye.
Digital tools also enhance patient-doctor collaboration. Mobile apps, for instance, enable individuals to track moles or skin changes over time, which they can share with their dermatologists. This promotes more proactive monitoring, leading to earlier intervention when skin cancer is detected.
Non-Invasive Treatment Innovations
Traditional skin cancer treatments often require surgery, ranging from minor procedures to major tissue removal. Advances in non-invasive treatments are changing this approach. These innovations are particularly effective for early-stage skin cancers and precancerous lesions.
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) has emerged as an effective option for treating certain types of skin cancer. This involves applying a light-activated medication to the affected area and exposing it to a specific wavelength of light. This process targets abnormal cells while reducing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Topical therapies are a modern advancement in treating skin conditions. Prescription creams like imiquimod or 5-fluorouracil are commonly used for superficial skin cancers. They allow patients to manage their condition at home while reducing the discomfort of invasive treatments.
Personalized Skin Cancer Treatments
Recent developments in personalized medicine have opened new doors in skin cancer care. Genomic testing is helping dermatologists and oncologists tailor treatment to each individual’s genetic profile. By analyzing the genetic mutations within the cancer cells, clinicians can prescribe targeted therapies, such as BRAF inhibitors for melanoma patients.
Immunotherapy has revolutionized treatment for advanced skin cancers. By stimulating the body’s own immune system to identify and attack cancer cells, immunotherapy offers a less intrusive alternative to traditional methods. Medications like immune checkpoint inhibitors are making strides in treating melanoma, even in cases previously considered difficult to manage.
Improved Patient Education
Advancements in technology and innovation are revolutionizing patient education in dermatology. Wearable devices like UV sensors now help users stay proactive by reminding them to apply sunscreen and tracking sun exposure, promoting preventative skin care habits. Advancements in technology have also lead to the rise of virtual consultations. This has made expert assessments and treatment recommendations more accessible than ever, eliminating the need for in-person visits. This is particularly beneficial for individuals in remote areas where access to dermatology services is limited, bridging the gap in care and encouraging better skin health for all.
Supporting Health With Dermatology Innovations
The rapid advancement of dermatology innovations represents a promising direction for skin cancer care. With tools and treatments that improve early detection, reduce invasiveness, and tailor therapies to individuals, patients now have greater access to options that align with their needs. The continuous evolution of these technologies not only enhances outcomes but also creates opportunities for more proactive and preventive care. For many, these advancements are becoming an integral part of managing their long-term skin health.