Headaches: Managing Stress and Its Impact on Migraine Frequency
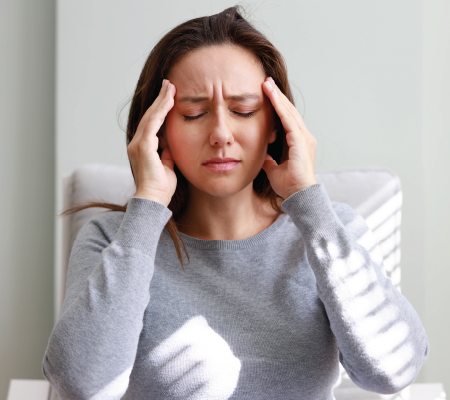

Migraine headaches are a common issue that can interrupt the lives of many individuals. While migraines can be triggered by various factors, stress is a dominant contributor. Learning how stress intertwines with migraine frequency and identifying ways to manage it can benefit those seeking relief. This article explores the relationship between stress and headaches, the impact on migraines, and potential approaches to mitigate its effects.
The Connection Between Stress and Migraines
Stress serves as a significant trigger for migraine headaches. When the body experiences stress, it may respond by releasing hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones are part of the body’s natural stress response but can lead to physiological changes, including vascular constriction or heightened sensitivity in the nervous system. Periods of stress may be followed by relaxation, known as the “weekend migraine” effect. During this time, the shift in cortisol levels can also stimulate a migraine episode.
Recognizing Stress-Induced Migraine Triggers
Individuals who experience migraine headaches may notice specific stress-related patterns in their daily lives. Some triggers may include:
- Deadlines or challenging work demands
- Major life events, whether professional or personal
- Sleep irregularities caused by stress
- Emotional strain, such as anxiety or worry
Identifying these patterns can help create proactive strategies to manage the triggers. Recording instances of stress and migraines in a headache journal, along with their circumstances, can help pinpoint links.
Practical Stress Management Techniques for Headaches
Several approaches can help manage stress levels and reduce the likelihood of migraines. These methods focus on promoting physical and emotional well-being. While not a treatment for migraines, integrating stress management practices into daily routines can support overall health and lower stress-induced episodes.
Incorporating Relaxation Techniques
Relaxation techniques can target physical responses to stress. Options may include deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and meditation practices. These approaches calm the nervous system, relax tense muscles, and stabilize cortisol levels. Individuals often find that setting aside even a brief period for relaxation aids in managing stress.
Regular Sleep and Consistent Routines
Creating a consistent sleep schedule can maintain hormonal balance and reduce stress levels. A quiet, dark sleeping environment, along with avoiding stimulants in the evening, can promote restful sleep. Developing regular bedtime rituals may also encourage relaxation as individuals prepare for sleep.
Physical Activity and Exercise
Physical activity can play a role in reducing stress by triggering the release of endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects. Aerobic exercise such as walking, swimming, or cycling may promote better stress responses. Stretching or yoga is another gentle option that combines physical movement with mindfulness for added relaxation.
Creative Hobbies and Social Connections
Engaging in hobbies that encourage creativity or spending time with supportive social networks can be calming. Activities such as painting, cooking, or having coffee with a friend can provide mental breaks from stress. In return, these activities help individuals feel recharged and more centered.
The Role of Professional Support
While self-management is often the first step for managing stress, reaching out to healthcare professionals can provide additional support. Therapists or counselors can teach cognitive coping strategies to address underlying stressors. For recurring migraine headaches, medical practitioners may provide customized guidance or recommendations regarding migraine prevention. Combining individual efforts with professional advice can often provide an effective support system for handling stress-induced migraines.
Take Charge of Stress-Related Migraines
Stress can influence both headache frequency and severity, making practical measures to reduce it a key component of migraine management. By identifying personal triggers and incorporating strategies such as relaxation, exercise, and consistent routines, individuals can take meaningful steps toward relief. If headaches persist or become disruptive, consider seeking professional advice to build a personalized approach.