Early Diagnosis of Hydrocephalus Why It’s Crucial for Treatment
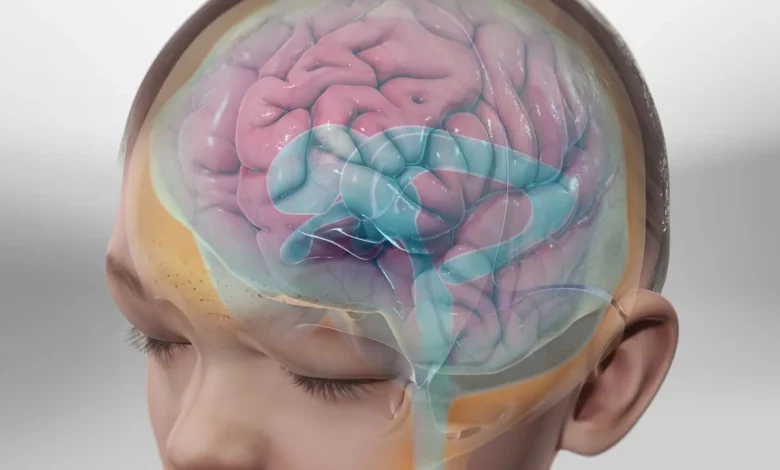
Hydrocephalus is a serious neurologic condition caused by an abnormal cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) buildup in the brain. It affects individuals of all ages, from infants to older adults. Early diagnosis of hydrocephalus is critical. Identifying the condition as soon as possible can significantly improve treatment outcomes and help prevent long-term complications. Understanding why early detection is vital for healthcare professionals, caregivers, and patients’ families is an important step toward better care.
What is Hydrocephalus?
Hydrocephalus occurs when there’s an imbalance between the production and absorption of CSF. They play a role in cushioning the brain and spinal cord, removing waste, and distributing nutrients. When this balance is disrupted, fluid accumulates in the brain, increasing pressure within the skull. This pressure can damage brain tissues over time.
Common symptoms of hydrocephalus vary by age group. Infants may experience rapid head growth, vomiting, and irritability. Older children and adults might show signs like headaches, blurred vision, difficulty walking, and memory issues.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
When hydrocephalus is diagnosed early, treatment can begin before the condition causes irreversible harm. Delayed diagnosis, on the other hand, often results in brain damage, developmental delays, or even life-threatening situations.
For infants, timely treatment can support normal brain development and reduce the risk of long-term complications. Identifying the condition early prevents further neurological deterioration and improves the quality of life for adults.
Early Warning Signs to Recognize
Recognizing symptoms early requires vigilance, especially for families and caregivers. Key warning signs to watch for include:
- Infants and young children
- The rapid increase in head size
- Bulging soft spot on the head (fontanelle)
- Poor feeding
- Persistent vomiting
- Older children and adults
- Persistent headaches
- Difficulty with balance or walking
- Cognitive decline or memory problems
- Urinary incontinence
If you observe any of these symptoms in a loved one, consult a healthcare professional immediately.
How is Hydrocephalus Diagnosed?
Diagnosing hydrocephalus involves a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging. Healthcare providers begin by thoroughly reviewing the patient’s medical history and symptoms. Imaging tests like ultrasoupatient’sfants), CT scans, or MRIs are key tools for confirming the diagnosis.
Doctors will also assess the root cause, as hydrocephalus can result from various issues like congenital abnormalities, infections, brain injuries, or tumors. Identifying the cause helps shape personalized treatment plans.
Treatment Options
The most common treatment for hydrocephalus is the surgical placement of a shunt system. This device directs excess fluid from the brain to another part of the body, such as the abdomen, where it can be absorbed. Alternatively, endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) may benefit certain cases, which allows CSF to flow generally without shunting.
Early diagnosis helps implement these options promptly, reducing the risk of complications and improving the patient’s recovery.
The Role of Awareness in Early Diagnosis
Patient education about hydrocephalus is crucial for early detection. Raising awareness among healthcare providers, educators, and families can bridge the gap between noticing early symptoms and seeking medical care. Support groups for caregivers and individuals with hydrocephalus also play an important role in promoting awareness and advocating for timely diagnosis.
Take Action Today
Hydrocephalus is a manageable condition, but early diagnosis makes all the difference. Recognizing symptoms and seeking prompt medical evaluation can protect your loved ones from potentially life-altering complications. If you suspect hydrocephalus in yourself or someone you care for, don’t hesitate to consult a medical professional. For caregivers and healthcare providers, continued vigilance and education are key in supporting patients on their path to recovery.